- Natto
- Health Benefits
Natto Health Benefits:
16 Things to Know About
Ask most Japanese people about natto health benefits and they'll tell you that these sticky, stringy beans are very healthy for the body.
In Japan it's common knowledge that natto is loaded with vitamins and minerals, and is healthy for your gut.
It's also known to have medicinal qualities and to help with fending off colds by keeping your immune system working as it should.
I enjoy eating fermented soybeans for the above reasons too, but natto gives our bodies so much more.
In fact, the more you learn about these sticky, stringy beans, the more you may want to eat them on a consistent basis.
That's definitely how I feel after learning more about these beans and I hope you will too.
In this article I share with you various nutrients and nutritional values found in natto, as well as highlight the health benefits these fermented soybeans give to our bodies.
Here are 16 Natto Health Benefits to know about that'll keep you eating, or at least get you thinking about eating, these sticky, stringy beans.
- Lecithin & Choline
- Saponin
- Isoflavones
- Dietary Fiber
- Vitamin E
- Protein
- Vitamin B6
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Calcium
- Vitamin B2
- Zero cholesterol
- Antibacterial effects
- Vitamin K2
- Nattokinase
Disclaimer: All the information in this article is published in good faith and for general information purpose only. If you wish to read in more detail about the various health benefits found in natto, you can follow the links in the "Sources" section in this article.
Natto Talk
Want to chat about Japanese fermented soybeans and how you can better enjoy this Japanese superfood?
Subscribe to Natto Talk!
A monthly publication containing info about:
- Things relating to natto
- Simply Natto's "Natto Recipe of the Month"
- Japan and its culture
- Updates made to the Simply Natto website and its social media pages
- Any upcoming product drops or projects
So what are you waiting for?
Fill out the form below and join.
I look forward to sharing my natto journey with you and learning about yours.

Simply Natto: Natto Lingo
健康に良い食品
(kenko ni yoi shokuhin)
"ken-coe-knee-yo-ee-show-coo-heen"
- a healthy food
ビタミン
(bitamin)
"bee-taw-mean"
- vitamin
Natto Health Benefits: Lecithin & Choline
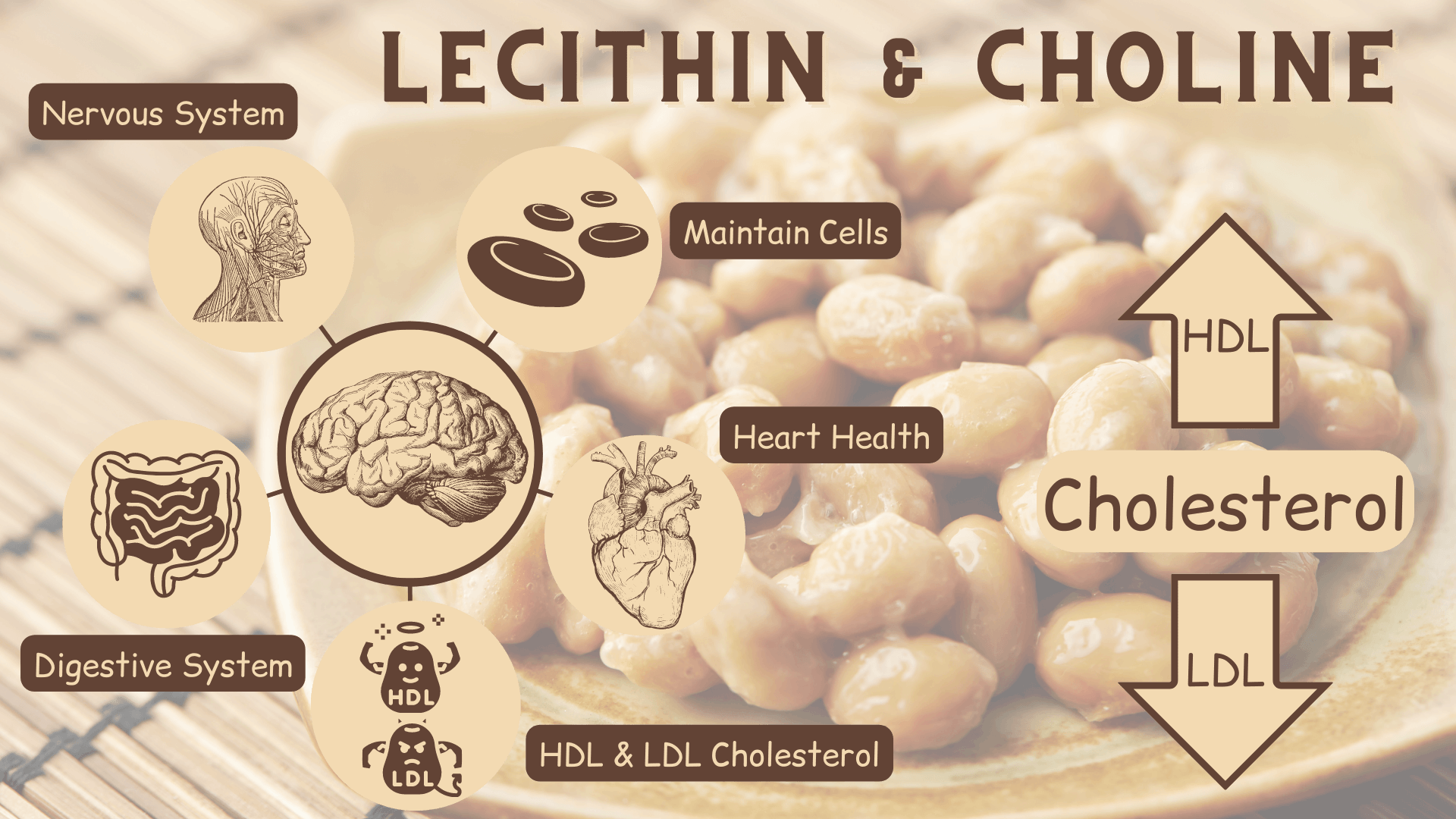
1. Lecithin & Choline
The first natto health benefit is lecithin, a group of chemicals found in soybeans and belonging to compounds called phospholipids.
Lecithin has been shown to raise "good" (HDL) cholesterol and lower "bad" (LDL) cholesterol, improve heart health, help improve digestion, and possibly help fight dementia symptoms (2).
Choline, which is found in Lecithin, is an essential nutrient that your brain uses to communicate (2) and that your body uses to transport fat, regulate metabolism, maintain cells, and help nerves transmit information (1).
Summary: Lecithin is found in soybeans and is a phospholipid containing the essential nutrient choline. Both lecithin and choline provide various health benefits for your cardiovascular system, your digestive system, your nervous system and your organs.
Natto Health Benefits: Saponin
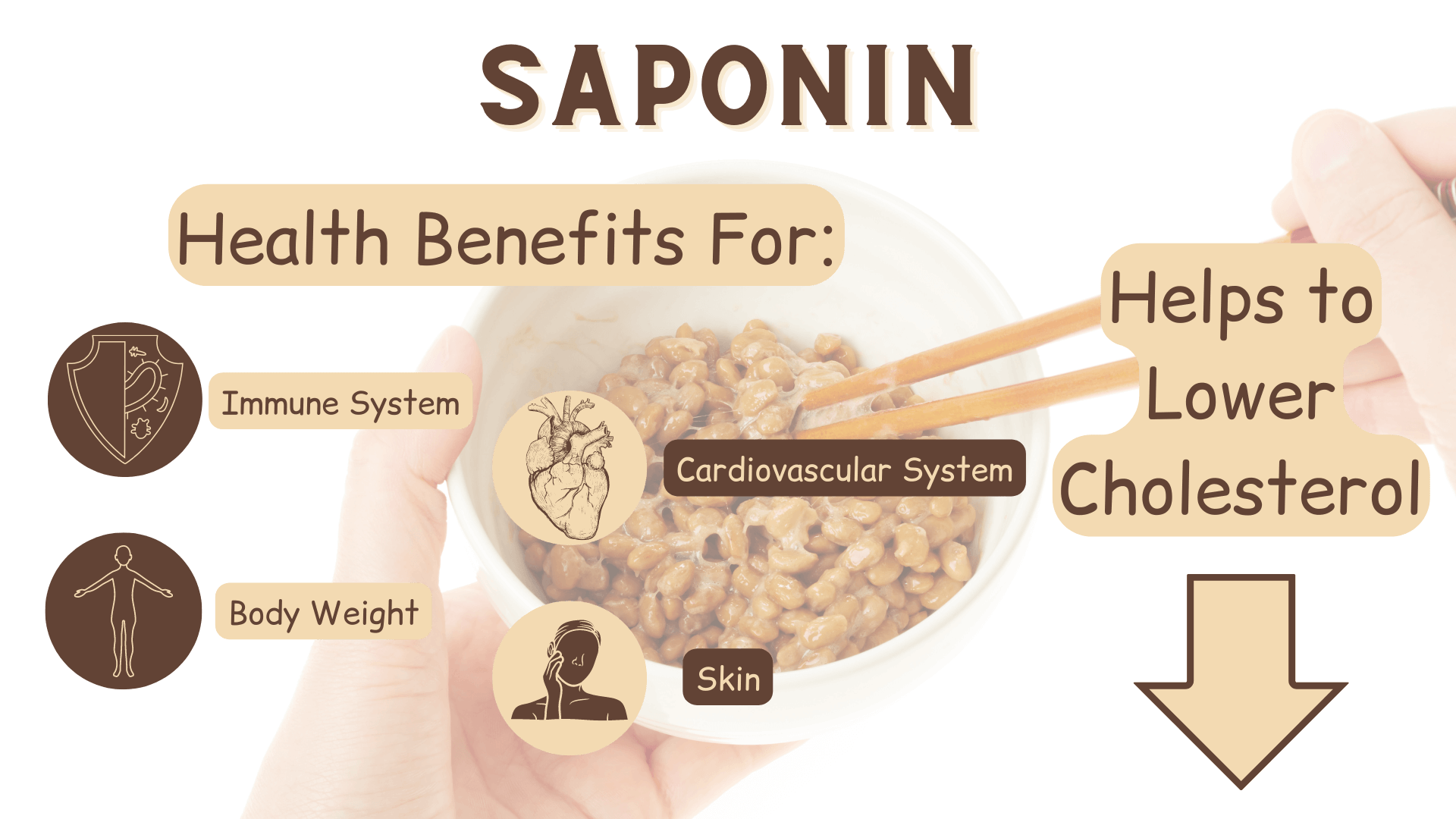
2. Saponin
The next natto health benefit is saponin.
This phytochemical is naturally found in soybeans and exhibits anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties, as well as antibacterial effects (3).
Saponins help to lower cholesterol (4), help your body absorb less fat from food, stimulate the production of T-cells, act as antioxidants and scavenge oxidative stress (3).
Summary: Saponins are naturally found in soybeans and provide various health benefits for your cardiovascular system, your immune system, your body weight and your skin.
Natto Goodness Fact: "Sapo" is Latin for soap, and when you add saponin to water it foams up. What happens to natto when it is mixed? It becomes sticky, stringy and foamy!
Natto Health Benefits: Isoflavones
3. Isoflavones
The third natto health benefit are isoflavones.
These flavonoids are found in soybeans and are classified as phytoestrogens.
These flavonoids exhibit antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties (5).
They have a similar structure to estrogen and they work in place of hormones when the release of estrogen decreases (6).
Summary: Isoflavones are flavonoids that are naturally found in soybeans and provide various health benefits for reinforcing your immune system, strengthening antibacterial and anticancer effects, and normalizing your hormone balance.
Natto Health Benefits: Dietary Fiber
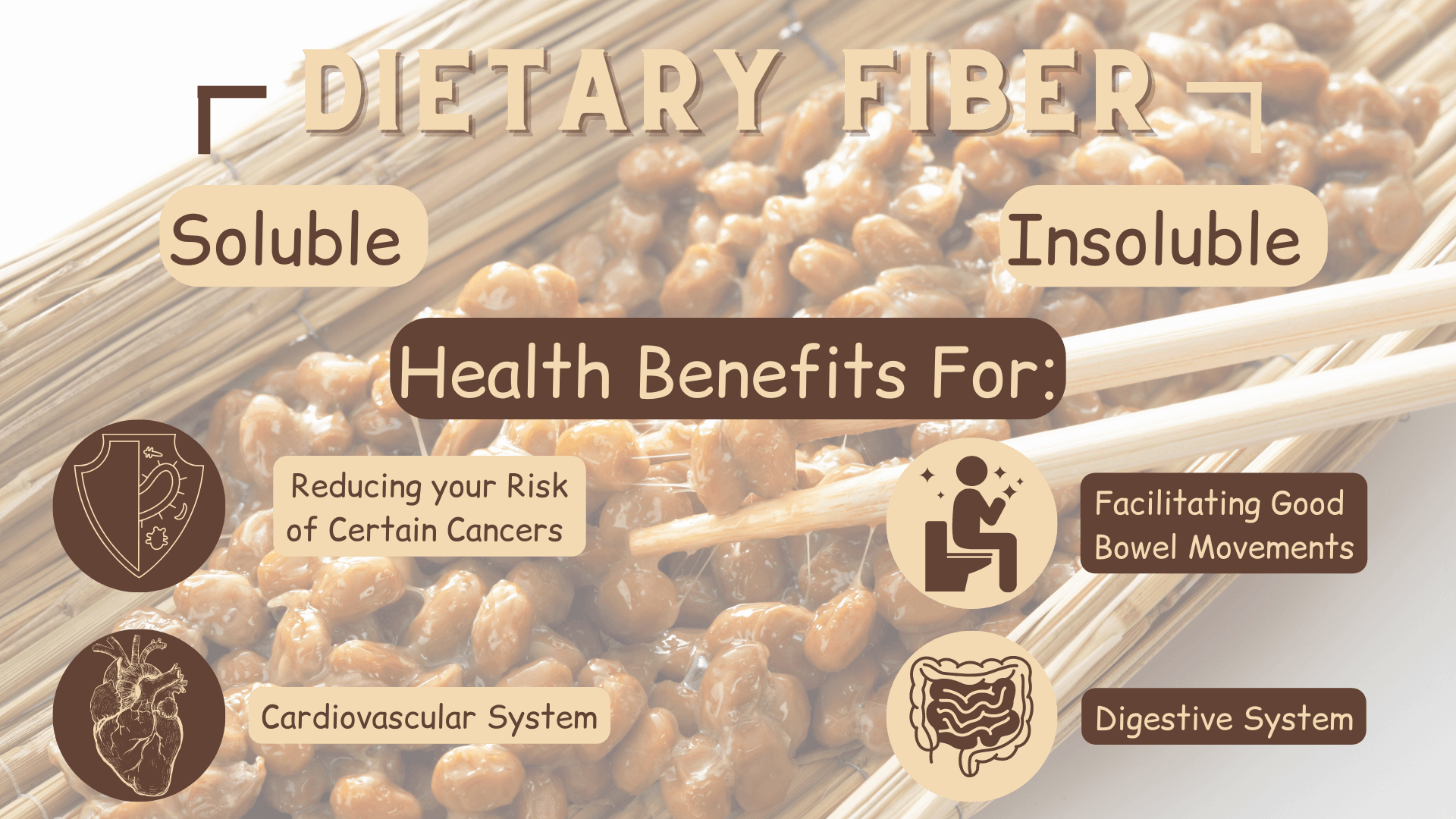
4. Dietary Fiber
The fourth natto health benefit is dietary fiber.
There are two types of dietary fiber: soluble and insoluble.
Dietary fiber is important for healthy digestion, for reducing your risk of certain cancers, and for lowering your risk of heart disease (10).
Cellulose is an insoluble fiber found in natto that helps to push food through your digestive system and support regular bowel movement (9).
Dietary fiber facilitates bowel movement by stimulating the intestinal walls and increasing good bacteria already in the intestines (7).
To facilitate bowel movement both types are needed, and natto contains a good balance of both (7)(8).
Summary: Soluble and insoluble are two types of dietary fiber naturally found in soybeans, and natto contains a good balance of both. Dietary fiber provides various health benefits for your digestive system, for reducing your risk of certain cancers, for your cardiovascular system, and for facilitating bowel movement.
Natto Health Benefits: More Fermented Soybean Goodness
Here are more natto health benefits from the various nutrients found in these stringy, sticky beans.
5. Vitamin E (11)
A nutrient that plays a role in improving vision, reproduction, and the health of your cardiovascular and neurological systems, and skin.
Vitamin E also has antioxidant properties.
6. Protein (12)
This macronutrient reduces hunger, helps you increase muscle mass and strength, is good for your bones, boosts metabolism and increases calorie burning, lowers blood pressure, helps your body repair itself after an injury, and helps reduce muscle deterioration.
7. Vitamin B6 (13)
This vitamin helps the body metabolize proteins and turns food into energy.
It helps in the creation of serotonin, dopamine, and hemoglobin.
Vitamin B6 is involved in immune system function, and it benefits the central nervous system.
8. Potassium (14)
This essential mineral regulates your heartbeat, ensures proper function of your muscles and nerves, and is vital for synthesizing protein and metabolizing carbohydrates.
It can also help keep blood pressure in a healthy range and lower stroke incidence.
9. Magnesium (15)
This mineral is essential for healthy bone formation, and for maintaining the health of your muscles, including your heart.
Magnesium helps with nerve function, regulating blood pressure, and supporting the immune system.
This mineral is needed for your body to produce hemoglobin.
It helps to preserve many vital functions in the body, including concentration and attentiveness, the immune system, and the regulation of body temperature.
Iron is also helpful for anemia, fatigue, and for restless leg syndrome.
11. Calcium (18)
This nutrient is essential for the development, growth, and maintenance of bone.
Calcium helps regulate muscle contraction, and it plays a key role in blood clotting.
12. Vitamin B2 (19)
This vitamin is also known as riboflavin, and it is essential for growth and overall good health.
Vitamin B2 helps to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, and plays an important role in maintaining the body's energy supply.
All of the above listed nutrients have health benefits for our bodies and have been recommended by health professionals and nutritionists to be consumed on a daily basis.
We get various nutrients from all of the different foods we eat on a daily basis, and by adding natto to our diet, we can get more of the necessary daily nutrients and our bodies can reap the benefits this Japanese micronutrient superfood provides.
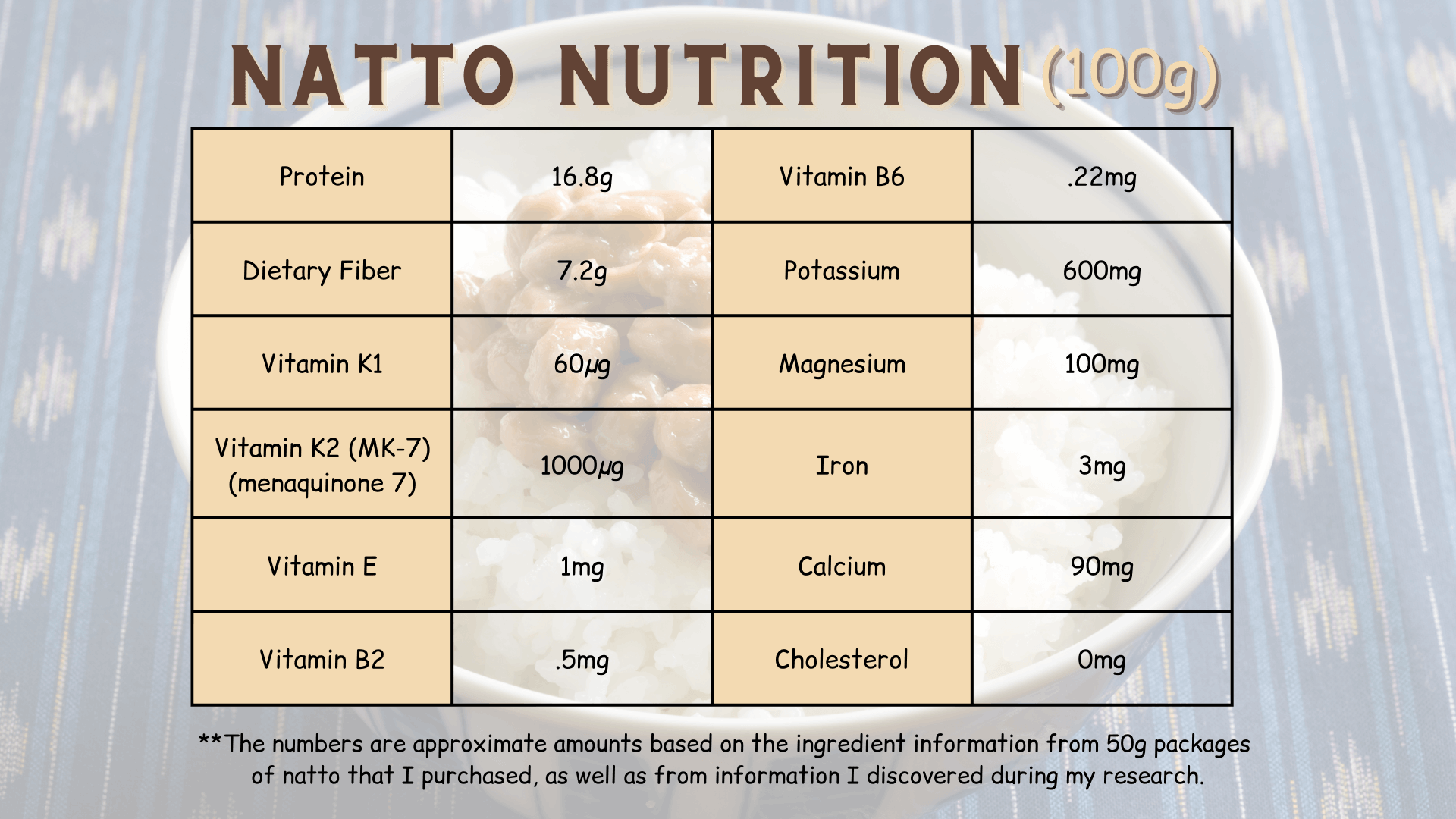
The table below shows the amounts of the daily nutrients found in 100g of natto.
**The numbers are approximate amounts based on the ingredient information from 50g packages of natto that I purchased, as well as from information I discovered during my research. Follow the links found in the "Sources" section for more detail (21) (24) (25) (26).
Looking For More Fermented Soybean Goodness?
Looking for more natto health benefits?
I've got you covered.
13. Zero Cholesterol (20) (21)
Natto has a high protein content like meat and fish do, but the difference is these sticky, stringy beans have zero cholesterol.
14. Antibacterial Effects (22) (23)
Natto has been found to have antibacterial and sterilizing effects.
Bacillus subtilis natto, the bacterium used to make natto, prevents pathogenic bacteria from growing, while the enzyme lysozyme works to do away with the bacteria.
In addition to these, natto also contains dipicolinic acid, which has been found to suppress Escherichia coli 0-157 (E. coli).
Saving the Best for Last!
Here are two more natto health benefits that really stand out.
The first is a vitamin found in natto with the highest concentration out of all other foods.
The second is an enzyme that's found only in natto.
Can I drop the microphone now?
I'll let you be the judge on whether that information is worthy of a "mic drop" or not, but at the very least I hopefully peaked your interest to learn more about these nutrients.
15. Vitamin K2
Japanese fermented soybeans have the highest amount of vitamin K2 out of all the foods rich in this nutrient, and you can discover more about K2 and the health benefits it provides the body by reading this article.
16. Nattokinase
Natto is the only food source of nattokinase, and you can read this article to discover more about this amazing enzyme and the health benefits it provides the body.
Bottom Line:
Natto is a Japanese micronutrient powerhouse loaded with vitamins, minerals and enzymes that provide the body with various health benefits.
Include these sticky, stringy beans in your diet by enjoying these traditional recipe ideas.
Or if you'd rather try something else, these unique recipe ideas are a tasty way to go.
If you're feeling adventurous read this article on how to make your own natto at home.
Keep up with the latest Natto Goodness by following Simply Natto on social media
The Latest Natto Talk
-
Natto Food with Sauces and Spices
Natto food with sauces and spices is a traditional and simple way for you to enjoy natto. It's a great way for you to savor some fermented soybean goodness. -
How to Make Wara Natto
Let's learn how to make wara natto. For centuries, Japanese natto has been made using rice straw, and now you can make it too. -
How to Make Natto with an All-In-One-Pot
Let's learn how to make natto! I'm going to show you how to make your own sticky, stringy beans using an all-in-one-pot. -
How to Make Hojicha Natto
Let's learn how to make hojicha natto! I'm going to teach you how to make your own sticky, stringy beans with a roasted green tea twist in 6 easy steps. -
How to Make Coffee Natto
Let's learn how to make coffee natto! I'm going to teach you how to make your own sticky, stringy beans with a java twist in 6 easy steps.
Sources:
(1): https://www.verywellhealth.com/lecithin-4771091
(2): https://www.healthline.com/health/lecithin-benefits#improves-heart-health
(3): https://healthyeating.sfgate.com/health-benefits-saponins-9131.html
(4): http://www.natto.or.jp/english/kenkou/daizu/dai04.html
(5): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4924202/
(6): http://www.natto.or.jp/english/kenkou/daizu/dai01.html
(7): http://www.natto.or.jp/english/kenkou/daizu/dai08.html
(8): https://www.otsuka.co.jp/en/health-and-illness/fiber/intake/foods-amount/
(9): https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/cellulose-fiber#what-is-it
(10): https://www.eatingwell.com/article/287742/10-amazing-health-benefits-of-eating-more-fiber/
(11): https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-e/art-20364144
(12): https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-reasons-to-eat-more-protein#TOC_TITLE_HDR_10
(13): https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219662
(14): https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-importance-of-potassium
(15): https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/286839#benefits
(16): https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/287228#benefits
(17): https://www.verywellhealth.com/iron-supplements-benefits-4178814
(18): https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/248958#why-we-need-calcium
(19): https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219561#Role
(20): http://www.natto.or.jp/english/hyakka/ped_zuno06.html
(21): http://www.takanofoods.co.jp/fun/cholesterol/
(22): https://www.jafra.gr.jp/eng/sumi.html
(23): https://suzuyokogyo.com/english/natto/about.html
(24): https://www.med.kindai.ac.jp/life/files/h23/2012022301_iki.pdf